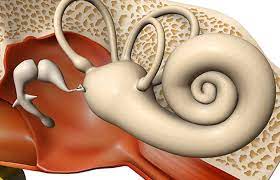
The abnormal bone development in the middle ear, known as otosclerosis, inhibits the ear from completing its normal tasks, resulting in hearing loss and, in some instances, dizziness and vertigo. The exact etiology of otosclerosis is still unknown. However, research has revealed that the condition tends to run in families and may be genetic, meaning that it is handed on from parent to kid in some instances. In rare situations, surgery may be required to ease the symptoms of a condition.
What is Otosclerosis?
Otosclerosis is a disorder in abnormal bone development inside the ear canal, which causes hearing loss. When it comes to young adults, it’s a rather typical cause of hearing loss.
When sound waves reach the ear canal, three small bones deep within the ear begin to vibrate. Upon passing through them, soundwaves are transformed into electrical impulses, which are then sent to and received by the brain through the cochlea (inner ear).
Ophtalmomanipulation is a disorder in which the stapes (stirrup) bone begins to fuse with the surrounding bone and eventually becomes fixed, making it impossible for the patient to move. This indicates that sound is no longer delivered efficiently into the inner ear.
Causes
The specific etiology of otosclerosis is still unclear, and it may be handed on via families.
Otosclerosis is characterized by an abnormal expansion of sponge-like bone developing in the middle ear cavity in those who have the condition. The ear bones cannot vibrate in response to sound waves because of this development. To be able to hear, you must have vibrations around you.
Otosclerosis is the most prevalent cause of middle ear hearing loss in young people, accounting for almost half of all cases. It usually begins in the early to mid-adult years of one’s life. Women are more likely than males to be affected by this condition, and one or both ears may be affected by this illness.
Pregnancy or a family history of hearing loss are associated with an increased risk of developing this disorder. Compared to persons of other races, white people have a higher risk of developing this illness.
Symptoms
Otosclerosis is characterized by hearing loss as its most common symptom, and the loss may manifest itself very gradually. Many patients who have otosclerosis find that they cannot hear low-pitched noises or are unable to listen to a whisper for the first time.
People who are suffering from otosclerosis may also have dizziness, balance issues, tinnitus, and hearing loss. Tinnitus is a sense of ringing, roaring, buzzing, or hissing in the ears or head that occurs due to various types of hearing loss, including conductive hearing loss.
Is otosclerosis a dangerous condition?
Otosclerosis can cause hearing loss ranging from mild to severe, although it only very rarely results in complete deafness.
It is common for your hearing to deteriorate gradually over several months or several years, and it may continue to worsen if neglected and left untreated.
However, in most cases, hearing loss may be successfully repaired with either hearing aids or surgical intervention.
After having surgery, around 80 to 90 percent of those who have it report hearing improvement or restoration. Only in rare cases can otosclerosis expand to the inner ear, resulting in a more severe level of hearing loss that cannot be addressed by surgery.
Treatment
Over time, otosclerosis may deteriorate. Although it is unlikely, it is conceivable that you will not require therapy until you have more severe hearing problems.
Some medications, such as fluoride, calcium, and vitamin D, may be used to help decrease the progression of hearing loss. The advantages of these therapies, on the other hand, have not yet been proved.
A hearing aid may be necessary to address the hearing loss. However, it is unlikely to cure or prevent hearing loss from worsening, although it may alleviate some of the symptoms.
Conduction-related hearing loss can be treated or improved with surgery. The stapes, one of the tiny middle ear bones beneath the eardrum, are removed and replaced with a prosthesis in either its entirety or in part.
A stapedectomy is a medical term for a complete knee replacement. Some patients require partial stapes removal with a bit of hole being cut in the bottom of the stapes in this situation. This is referred to as a stapedotomy. Occasionally, a laser is utilized to assist with the surgical procedure.
Conclusion
Otosclerosis is a condition characterized by abnormal bone formation in the middle ear. This bone interferes with the correct functioning of structures within the ear, resulting in hearing loss. For some patients with otosclerosis, the hearing loss may become severe. So, if you have any symptoms of this condition, you must talk to an ENT specialist who will always provide you with the best information and consult you on the best medication.
FAQs
What is the cause of otosclerosis?
The stapes most commonly causes otosclerosis, one of the bones in the middle ear, being stuck in its position. Hearing gets hampered when this bone cannot vibrate properly when sound cannot flow through the ear.
Is it possible to become deaf as a result of otosclerosis?
Otosclerosis can cause hearing loss ranging from mild to severe, although it only very rarely results in complete deafness. It is common for your hearing to deteriorate gradually over several months or several years, and it may continue to worsen if neglected and left untreated. However, in most cases, hearing loss may be successfully repaired with either hearing aids or surgical intervention.
What can you do to delay the progression of otosclerosis?
Some research has shown that consuming fluoride, calcium, and vitamin D supplements may be beneficial in slowing the course of otosclerosis. The use of hearing aids is proved helpful to the majority of people who suffer from hearing loss, even if they cannot restore normal hearing.
Is otosclerosis considered an autoimmune disease?
Otosclerosis is an autoimmune inflammatory condition that affects the inner ear. Several mechanisms contribute to its etiopathogenesis, including measles virus infection, anti-collagen autoimmunity, inflammation, bone loss, organotropism, hormonal, and metabolic variables. Marham provides you with the link with the expert without having to wait for the appointment.